2 min to read
reproducing cve-2013-2028

嗯,最近打 d^3ctf 的时候,就遇到了一个 cgi 的题是复现一个 1-day fast cgi 漏洞,虽然这是我 CTF 生涯中很少见的几次用 1-day 出题,但是感觉复现漏洞能力还是非常关键,而且涉及到供应链安全
然后做网安导作业的时候,遇到了这个复现 cve-2013-2028 的 challenge,嗯,其实去年的时候就遇到了,那个时候刚打完 XCTF FINAL,是在和造编译器的伙伴们 hangout 的时候尝试的,当时并没有跑起来现成的 exp,今年在杰哥的帮助下成功复现,还是学到了很多,在这里记一下
主要源码是参考的 这个仓库 其实个人遇到的主要是两个问题,第一个是如何以正确的 local address, remote address 跑起来该 exp,第二个是如何调试
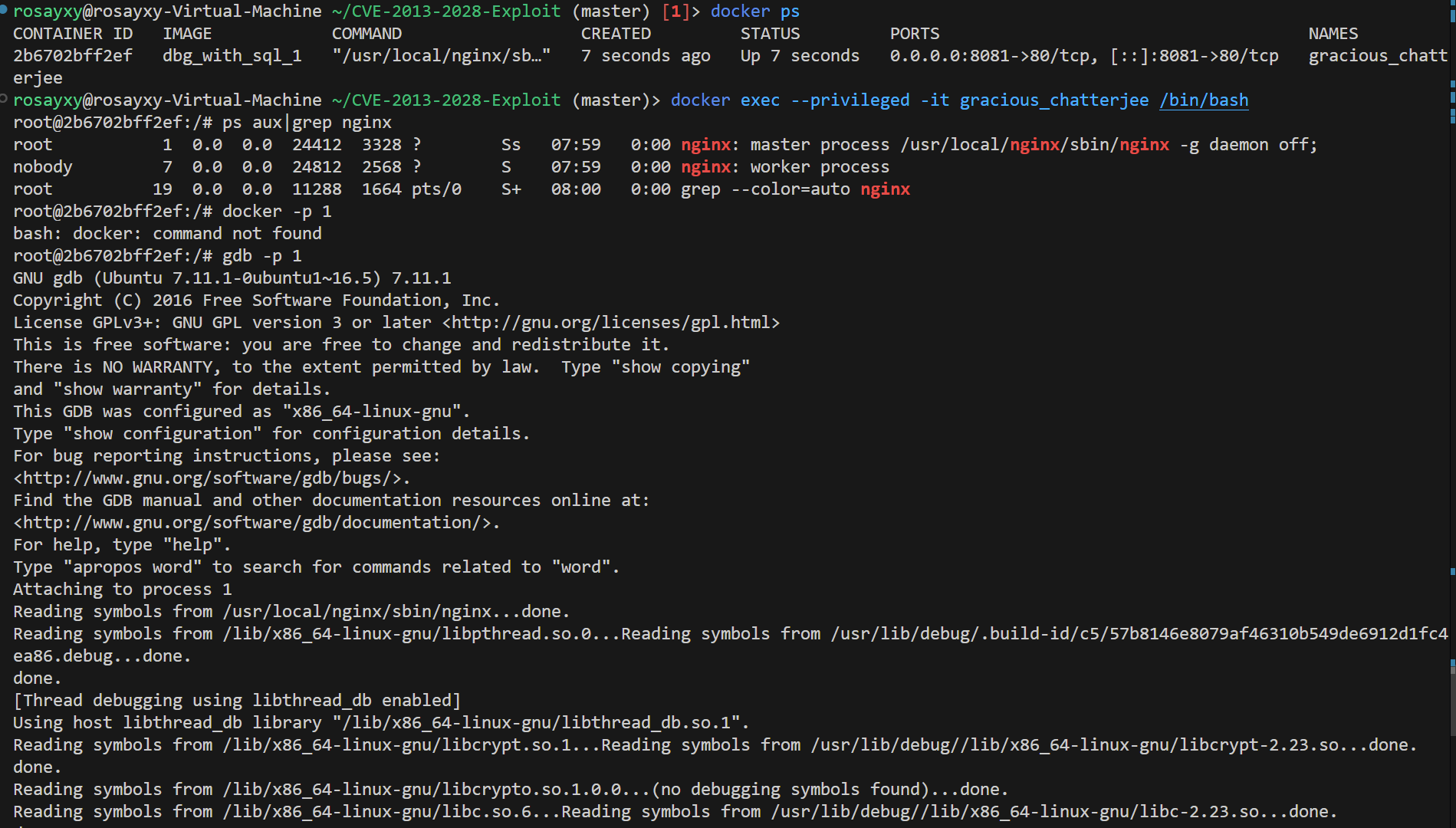
确定 remote host ip address, listener ip address
通过 docker ps 确定跑起来的 container,然后 docker inspect <container_id> 查看网络配置,找到 IpAddress GateWay 字段,分别表示 remote host ip address 和 listener ip address
debug
我们发现脚本跑起来以后还是不能反弹 shell,canary 可以爆破出来,猜测是 rop 中有些地址和之前的 release 版本地址不一致,从而产生了 crash
我们思路是在 Docker 里面 gdb -p <pid> attach 上 nginx 的进程上,然后 r 运行到 crash 的位置,看栈上的 ROP chain 是否正确
然后需要分两次爆破 canary 和打 ROP,不然会难以把控 gdb attach 的时机
如图为调试输出,可以看到寄存器和 stack 的情况
我们发现是 mprotect 函数的地址不对,它是通过 libc_relative_addr + offset 来计算的,我们调整一下 offset 就行了
具体的指令是
docker ps
docker exec --privileged -it <container_id> /bin/bash
ps aux|grep nginx
docker -p 1
set follow-fork-mode child # 跟踪子进程
b mprotect # 通过输出查看 mprotect 的位置,像是 `Breakpoint 1 at 0x7528de82e870: file ../sysdeps/unix/syscall-template.S, line 84`
analysis
基本分析见这个链接
调用链大概如下
ngx_http_read_discarded_request_body
ngx_http_discard_request_body_filter
ngx_http_parse_chunked (vulnerable function)
然后基本的 dataflow 如下
ngx_http_read_discarded_request_body(r):
loop:
size = ngx_min(r->headers_in.content_length_n,
NGX_HTTP_DISCARD_BUFFER_SIZE) // since this is signed comparison, if content_length_n is bigger than INT64_MAX, size will be negative, so the size will be a negative value
n = r->connection->recv(r->connection, buffer, size) // size is negative, and will be cast to unsigned type, so it will receive a very large amount of data and cause a stack overflow
// ......
rc = ngx_http_discard_request_body_filter(r, &b)
ngx_http_discard_request_body_filter(r,b_ptr):
if r->headers_in.chunked:
loop:
rc = ngx_http_parse_chunked(r, b, rb->chunked)
if rc == NGX_AGAIN:
r->headers_in.content_length_n = rb->chunked->length // this can be bigger than INT64_MAX too
ngx_http_parse_chunked(r, b, ctx):
ctx->size = A_VALUE_BIGGER_THAN_INT64_MAX // vulnerability
ctx->length = ctx->size + const
reproduce
此外,就是看我们怎么满足到达这些代码所需要的分支条件了(唉 回想起来复现 cve-2023-21768 的时候 也是差不多的操作 笑死)
首先在 ngx_http_discard_request_body_filter 函数里面,需要 ngx_http_parse_chunked 的返回值为 NGX_AGAIN 这就需要我们在 overflow 之前输入的那个 chunk (4096 bytes 的连续字节) 不存在 LF 字符,且 size 字段可以被解析为负数,这个是在脑子里符号执行分析出的 xs
thinking like a pwner
why can we bruteforce canary this time?
出学 pwn 的时候,记得轩哥教过“一般只有题目给你条件爆破 canary 的时候,你才能爆破 canary”,比较经典的做法是
- 利用题目的逻辑漏洞之类的 leak canary
- 利用任意地址写写
fs:0x28的值,然后覆盖 canary 的值和它一样来 bypass 检查 - bruteforcing thru fork, just like in this writeup
而我们现在就是用第三种情况来 leak canary, 主要利用的点是 child process 挂掉并不会影响 parent process 的状态(而非 fork 的情况下,每次猜测 canary 如果猜错了,那重启之后 canary 就不一样了),所以就方便逐位爆破了
possibility of automated discovery
这个漏洞的类型属于整数溢出,但是可以看到从漏洞点到利用点还是有一些距离,理论上可以通过 taint analysis 来解出,而 CodeQL 可以用来实现有源码的 taint analysis 检测,具体可以类比看我们能否控制 memcpy, memmove 这种函数的 size 的情况,我们去判断 source 和 sink 点,source 为我们解析出 ctx->size 的位置,sink 点为 recv 的地方,用 taint 的方法看 source 和 sink 点之间是否有 dataflow
或者可以直接上 fuzz 来找洞,也是比较通用的方法 (TODO 可以试一下),他有一个经典 http 状态机,可能直接用 afl/REDQUEEN 这种简单的编译策略可能不太能 fuzz 出来感觉,倒是可以上一些对 state 更敏感的 fuzzer 来玩,就像我们组博栋师兄的 statefuzz
integer overflow
就像 ctf 里面一样,总得检查一遍比较是 signed 还是 unsigned 类型,只能说 signed 类型的比较更 conducive to bugs 吧 笑死,这种小地方确实不容易注意到orz
对于这个漏洞,他之所以能让 size 是负数主要是因为解析时是这样写的
ctx->size = ctx->size * 16 + (ch - '0');
该例子可以用 rust 的 Wrapping 方法来检测溢出到负数,像是 wrapping_mul 之类的,见 this link
Comments